Compression moulding is a rather complex process, but understanding how it works can help you better appreciate the overall advantages of its use in making both heavy and light goods. It is generally thought that the process is rather simple, however it’s a crucial one as it determines the properties of the end product. For example, an inner plaster layer of moulded foam will stop the air from travelling up through the piece of rubber, while still allowing it to exit the other side. However, while this is an obvious benefit, what isn’t so clear is how the moulded material changes the properties of the rubber.
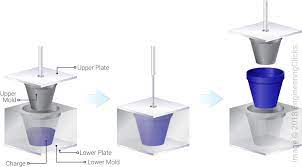
The key feature of how compression moulding works is its use of heat and/or cold to change the properties of the rubber. The type of mould to be used, then, depends on how each attribute reacts to these two factors. Firstly, heat is used to melt the glue that holds the rubber components together. Once the glue is liquefied, the mould is able to pass through the interior of the shell, flattening it out as it goes. This causes some of the inner surface of the rubber to be pulled away, reducing the overall thickness of the piece of rubber. For Rubber Moulding services, visit Meadex

Finally, pressure is applied to the mould, pressing the moulded material against the interior surface of the shell. In order to understand how compression moulding works, then, it’s important to look at how the moulded materials travel through the moulds. The moulds are positioned inside the chamber that contains the liquid material. As the material passes through the mould, it forces the inner surface of the material upwards, flattening it out and making it easier for the pressed material to travel through the mould. The compression molding process is therefore essential for making any interior surface of a product uniform.



















